What is Personalization in UX?
Personalization in UX involves adapting and customizing a user experience on a website or platform to a user’s specific preferences, needs, and behavior. This can be done through techniques such as recommending relevant content, customizing the layout or design, or adjusting the functionality to meet the user’s needs. By doing so, personalization can enhance the user’s experience by making the website or platform more relevant, efficient, and intuitive for them.
With every interaction being monitored to improve the user experience, this trend represents a significant advancement in user satisfaction. For instance, Google displays the nearby parking possibilities near your usual work location; Netflix provides recommendations based on what you have already watched, and chatbots offer customized responses to your specific questions.
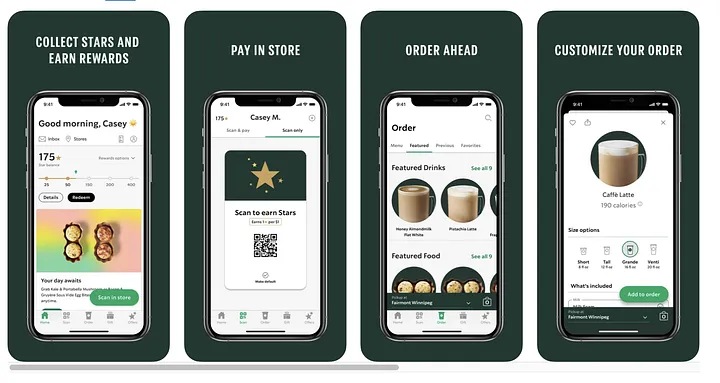
Starbucks’ smartphone app for online ordering is designed to recognize users’ purchasing habits and preferences by tracking previous orders. Users can choose from a list of items that they’ve already ordered rather than having to browse the entire menu, which simplifies the ordering process for them.
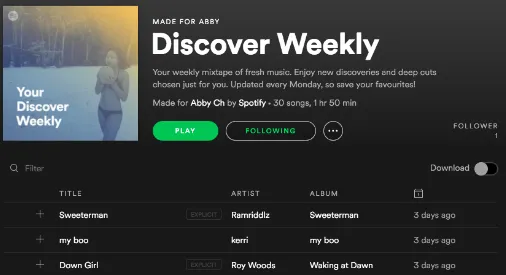
Spotify is among the best examples of a service that does this well. Based on your listening history, they can recommend songs and albums that go perfectly with the music you like the most. It has become a pretty popular feature. Within the first year of operation, Spotify declared that 5 million songs had been listened to by 40 million users.
Let’s see some stats and facts
- 47% of consumers check Amazon if the brand they’re shopping with doesn’t provide product suggestions that are relevant. — SmarterHQ
- 74% of consumers say “living profiles” with more detailed personal preferences would be useful if they were used to curate personalized experiences, products, and offers. — Accenture
- 70% of consumers say that a company understanding how they use products and services is very important to winning their business. — Salesforce
- When customers receive transparent ads based on their activity on a site, the revenue of the product grows by 38%. — Harvard Business Review
- Consumers are 2.1x more likely to view personalized offers as important versus unimportant. — Salesforce
- 59% of consumers say personalized engagement based on past interactions is very important to winning their business. — Salesforce
(Source — Forbes 50 Stats Showing The Power Of Personalization)
Types of personalization
There are broadly two categories of personalization based on the information collected by the user- explicit and implicit personalization. Let’s take a detailed look at both of them.

Explicit Personalization
Explicit personalization involves using specific information about a visitor to customize their experience on a website. Using particular information about a visitor to a website to alter their experience is known as explicit customization. Forms, surveys, or polls that ask visitors for personal information can be used to collect this data.
A website might, for instance, invite a visitor to identify themselves as a parent, alumni, potential students, or present students. Based on this data, the website can display personalized content and alter the primary copy, navigation, and other features to better meet the requirements and preferences of its users.
Implicit Personalization
The basis for this type of customization includes the device being used to access the website, the visitor’s location, and their online activity while on the page. The user experience of a website, for instance, may be tailored according to the device the visitor is using or the visitor’s geographic location.
A website may also personalize a visitor’s experience by using information about their online activities, such as the pages they have viewed or how frequently they have visited. For instance, a website might use this information to present tailored CTAs (call-to-action) or to show visitor-relevant success stories or testimonials.
Implicit personalization is further classified into different categories:
1. Context-Aware Personalization
Context-aware personalization makes use of information from previous user interactions and behavior to craft a customized experience that adapts to each user’s unique interests and preferences.
Google Maps: Google Maps uses data about a user’s past searches and locations to provide personalized recommendations for places to go and things to do. It also allows users to share their location with friends and family and provides personalized location-sharing options based on the user’s past location-sharing activity.
2. Content-Based Personalization
It involves providing content to users based on what they have previously interacted with. This type of personalization can be used to suggest similar content that a user may enjoy.
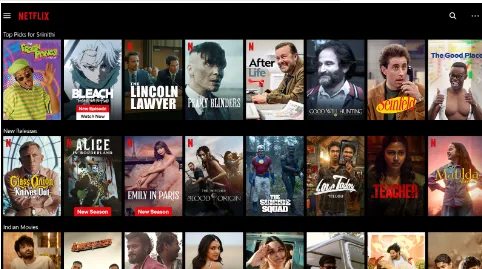
Netflix: Netflix uses algorithms to analyze a user’s viewing history & preferences, and then uses this data to provide personalized recommendations for TV shows and movies that the user might be interested in. Netflix also allows users to create multiple profiles and their playlists within a single account and uses data from each profile to personalize the content that is recommended to that user.
3. Location-Based Personalization
It considers a user’s geographic location to provide a more individualized experience. Region-specific content and recommendations can be offered through this kind of personalization.
Zomato: Zomato uses location-based personalization by sending push notifications in regional languages and increased their sales a lot more than from the traditional notifications.
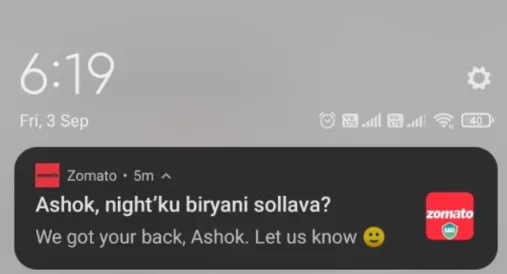
4. Behavioral Personalization
Using behavioral personalization, content can be tailored to the user and more relevant recommendations can be made by keeping track of their online activity, such as the pages they frequently visit and the things they show interest in.
Starbucks: Starbucks uses AI technology to analyze customer data and preferences to create customized offers and experiences for each individual. This personalized approach not only helps to build customer loyalty and retention but also helps to create a more positive and enjoyable experience for customers when they visit Starbucks. Additionally, the use of AI to send personalized messages to customers demonstrates Starbucks’ commitment to using technology to enhance the customer experience and stay ahead of the curve in the fast-paced world of retail.
5. Social Personalization
Social personalization allows for the customization of content and recommendations based on a user’s social media activity and interests.
Social personalization can also be used to target advertising to specific users or groups of users based on their social data and connections. It also provides personalized recommendations for content, products, or services based on a user’s social connections and interactions. For example, a social media platform might use data about a user’s friends and their interests to recommend new pages or groups to join.
Difference between Personalization and Customization
Personalization is when a company uses the data and information they have access to of their customers’ behaviors, preferences, needs, and shopping patterns to offer a personalized experience to individual users.

Pros of Personalization
- Personalization is an automated process that requires little effort from either the product or the user.
- A personalized website that recognizes user preferences can not only display the desired information or content, but can also improve conversions and engagement by providing a more tailored experience.
- Personalization can be implemented on a larger scale than customization, offering the potential to reach a wider audience with tailored content. However, it is important to consider the resources and effort required to implement personalization and to balance it with the benefits it offers to users.
Cons of Personalization
- Privacy concerns can lead some individuals to feel uncomfortable with highly customized and personalized websites.
- Customization is a developing field of technology, and creating and maintaining a completely customized website may be challenging.
- Inconsistencies in the deployment of customization can distract and deter users rather than encourage them to return. It is important for businesses to consider the potential impact on user privacy and to balance the benefits of customization with the resources and effort required to implement it.
Customization refers to the user’s ability to customize or personalize particular features of their experience. This can include options to modify a website’s or app’s design or layout, configure notification or alert preferences, and decide which features or functionalities to enable or disable. Instead of relying on the system to cater the experience to their requirements and preferences, customization enables the user to do it themselves.
Pros of Customization
- Customization allows users to take control of their experience on your platform, enabling them to choose what they want to see and how they want to engage with your platform in a privacy-friendly manner.
- Customization is typically easier to implement than full-scale personalization. However, it is important to consider the resources and effort required to implement customization and to balance it with the benefits it offers to users.
Cons of Customization
- Customization requires a significant amount of effort from users, as they must set their preferences and personalize their experience, considering their likes and dislikes and filtering out irrelevant content.
- Can be time-consuming and may be challenging for users who are unsure of what they want or how to use the platform.
- While customization is an effective way to give users exactly what they want, it can also be costly to implement and may be limited in scope compared to personalization.
- It doesn’t allow for as much flexibility as personalization and the potential of infinite ways to tailor content to individual users. However, it is important to balance the benefits of customization and personalization with the resources and effort required to implement them.
Both personalization and customization can help enhance the user experience, but they have various functions and applications. While customization enables users to have more control over their experience, personalization may be more effective at providing tailored experiences to specific users.
Every visitor is different, and as far as customization and personalization are concerned, knowing your target audience is the key to success in both cases. Also, considering the fact that both these techniques constantly demand maintenance, personalization, despite its cons, is taking over customization in every possible aspect.
Conclusion
Personalizing the user experience is a key aspect of design that helps companies deliver more tailored, satisfying, and loyal experiences to their users. This can be achieved through various means such as predictive analytics, personalized content, chatbots, micro-interactions, and gamification, all of which aim to make the user experience more engaging and enjoyable. By leveraging data and technology, companies can create a more personalized user experience that meets the unique needs and preferences of their customers.
Reference Links
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/blakemorgan/2020/02/18/50-stats-showing-the-power-of-personalization/?sh=9048b292a942
- https://www.indigo9digital.com/blog/starbucksmobileapps
- https://www.nngroup.com/articles/customization-personalization/
- https://www.netsolutions.com/insights/how-to-take-your-ux-to-a-new-level-with-personalization/
- https://uxstudioteam.com/ux-blog/personalized-experience/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/blakemorgan/2021/03/29/the-20-most-compelling-examples-of-personalization/?sh=66f1aa8b71b1
- https://vwo.com/website-personalization/